
Hydrogen
Chemical reactions
Reaction of hydrogen with acidsHydrogen, H2, does not react with dilute acids.
Reaction of hydrogen with airHydrogen, H2, does react with oxygen, O2, unless ignited with a flame or a spark (and the mixture is the right ratio). The reaction is a fire or explosion, depending on the conditions, with a characteristic reddish flame.
2 H2(g) + O2(g)  2 H2O(g) 2 H2O(g)Nitrogen can be brought to react with hydrogen. This is called the Haber process [5]: N2(g) + 3 H2(g) 400-500 °C 2 NH3(g)Fe catalyst  High pressure Reaction of hydrogen with basesHydrogen, H2, does not react with dilute bases.
Reaction of hydrogen with halogensHydrogen, H2, reacts with halogens, forming hydrogen halides. The reactions are slow at room temperature, except for fluorine and increases in speed with increasing temperatures. The reaction with fluorine is fast, even at room temperature. Under some conditions, the reactions with fluorine and chlorine can be explosive [5].
H2(g) + F2(g)  2 HF(g) 2 HF(g)H2(g) + Cl2(g)  2 HCl(g) 2 HCl(g)H2(g) + Br2(g)  2 HBr(g) 2 HBr(g)H2(g) + I2(g)  2 HI(g) 2 HI(g)Reaction of hydrogen with metals/metal ionsHydrogen reacts with alkali metals and calcium, strontium and barium, forming hydrides [5]:
2 Li(s) + H2(g)  2 LiH(s) 2 LiH(s)2 Na(s) + H2(g)  2 NaH(s) 2 NaH(s)2 K(s) + H2(g)  2 KH(s) 2 KH(s)2 Rb(s) + H2(g)  2 RbH(s) 2 RbH(s)2 Cs(s) + H2(g)  2 CsH(s) 2 CsH(s)Ca(s) + H2(g)  CaH2(s) CaH2(s)Sr(s) + H2(g)  SrH2(s) SrH2(s)Ba(s) + H2(g)  BaH2(s) BaH2(s)Cd usually does not react with H2(g). At 450 °C H2 is adsorbed in the metal. When the metal has reached max. adsorption the temperature will increase and Cd reacts with H2 [4]. Cd(s) + H2(g) 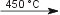 CdH(s) + H· CdH(s) + H·Hydrogen does not react with gold, platinum and tungsten, but is dissolved in the metal instead [5] Hydrogen reduces some metal oxides [5]: Fe3O4(s) + 4 H2(g)  3 Fe(s) + 4 H2O(g) 3 Fe(s) + 4 H2O(g)MnO4(s) H2(g)  MnO(s) + H2O(g) MnO(s) + H2O(g)Reaction of hydrogen with sulfurSulfur reacts with hydrogen, forming hydrogen sulfide [5]:
S8(s) + 8 H2(g)  8 H2S(g) 8 H2S(g)Reaction of hydrogen with waterHydrogen does not react with water, but it is slightly soluble in water (1.6 mg/l (20 °C) [2])
|