
Cadmium
Chemical reactions
Reaction of cadmium with acetic acidCd reacts slowly with gaseous acetic acid [5].
Reaction of cadmium with airUnder normal pressure and temperature, Cd does not react with the air. Polished Cd is matted after a while, forming CdO [5].
At 300 °C Cd forms a thin brown gas-permeable coating. The yield increases parabolic with temperature [5]. Cadmium metal burns in air to form cadmium(II)oxide. The burning temperature is above the sublimations temperature of CdO, 1385 °C [5]. 2 Cd(s) + O2(g)  2 CdO(s) 2 CdO(s)Reaction of cadmium with ammoniaCd does not react with NH3 in its gaseous form until 255 °C. Above 255 °C is unknown. In aqueous solution NH3 dissolves Cd. Cd2+ forms complexes with NH3(aq). The average number of NH3 per Cd is four but varies depending on [Cd2+] and [NH3] [5].
Cd(s) + NH3(g)  Cd(s) + 4 NH3(aq)  Cd2+(aq) + ?? Cd2+(aq) + ??Cd2+(aq) + 4 NH3(aq)  [Cd(NH3)4]2+(aq) [Cd(NH3)4]2+(aq)Reaction of cadmium with arsenicGaseous arsenic reacts with solid Cd forming Cd3As2 at around 700 °C [5].
3 Cd(s) + 2 As(g)  Cd3As2(s) Cd3As2(s)Reaction of cadmium with halogensCd(s) + F2(g)
 CdF2(s) [white] CdF2(s) [white]Cd reacts directly with Cl2 in aqueous solution [5]. Cd(s) + Cl2(aq)  Cd2+(aq) + 2 Cl−(aq) Cd2+(aq) + 2 Cl−(aq)Cd reacts directly with Br2 in aqueous solution and Br2(g) at 450 °C [5]. Cd(s) + Br2(aq)  Cd2+(aq) + 2 Br−(aq) Cd2+(aq) + 2 Br−(aq)Cd(s) + Br2(g)  CdBr2(s) [pale yellow] CdBr2(s) [pale yellow]Solid Cd does not react with I2(g), but will react with I2(aq). In gas phase Cd and I2 will react forming CdI2. At high temperature and pressure (e.g. a steel bomb) equivalent Cd and I2 will react forming CdI [5]. Cd(s) + I2(aq)  Cd2+(aq) + 2 I−(aq) Cd2+(aq) + 2 I−(aq)Cd(g) + I2(g)  CdI2(g) CdI2(g)2 Cd(g) + I2(g) 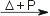 2CdI(g) 2CdI(g)Reaction of cadmium with hydroxideMetallic cadmium does not dissolve in aqueous alkalis such as potassium hydroxide, KOH. Cd2+ is precipitated by excess amounts of OH− at pH > 7.5 [5]
Cd(s) + OH−(aq)  Cd2+(aq) + 2 OH−(aq)  Cd(OH)2(s) Cd(OH)2(s)Reaction of cadmium with hydrobromic acidCd reacts with hydrobromic acid forming CdBr2 [5].
Cd(s) + 2 HBr(aq)  CdBr2(s) + H2(g) CdBr2(s) + H2(g)Reaction of cadmium with hydrochloric acidCd reacts with hydrochloric acid forming CdCl2 [5].
Cd(s) + 2 HCl(aq)  CdCl2(s) + H2(g) CdCl2(s) + H2(g)Reaction of cadmium with hydrofluoric acidCd reacts with hydrofluoric acid forming CdF2 [5].
Cd(s) + 2 HF(aq)  CdF2(s) + H2(g) CdF2(s) + H2(g)Reaction of cadmium with hydrogenCd usually does not react with H2(g). At 450°C H2 is adsorbed in the metal. When the metal has reached max. adsorption the temperature will increase and Cd reacts with H2 [5].
Cd(s) + H2(g) 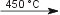 CdH(s) + H· CdH(s) + H·Reaction of cadmium with hypochloriteCd reacts with hypochlorite forming Cd(ClO2)2 and after a while also Cd(ClO3)2 [5].
Cd(s) + 2 HClO2(aq)  Cd(ClO2)2(s) + H2(g) Cd(ClO2)2(s) + H2(g)  Cd(ClO3)2(s) Cd(ClO3)2(s)Reaction of cadmium with nitric acidCd does not react with the fumes from concentrated nitric acid [5].
Cd(s) + HNO3(g)  Dilute hot nitric acid will dissolve Cd, forming nitrogen monooxide 3 Cd(s) + 2 NO3-(aq) + 8 H+(aq)  Cd2+(aq) + 2 NO(g) + H2O(l) Cd2+(aq) + 2 NO(g) + H2O(l)Reaction of cadmium with phosphorusCd reacts with P at elevated temperatures in an exoterm process forming Cd3P2 and CdP2 [5].
4 Cd(s) + P4(s)  Cd3P2(s) + CdP2(s) Cd3P2(s) + CdP2(s)Reaction of cadmium with ortho- and pyrophosphoric acidCd2+ is precipitated by ortho- and pyrophosphoric acid in an acetic acid/acetate-buffer [5].
3 Cd2+(aq) + 2 PO43−(aq)  Cd3(PO4)2(s) Cd3(PO4)2(s)3 Cd2+(aq) + P2O74−(aq) + H2O(l)  Cd3(PO4)2(s) + 2 H+(aq) Cd3(PO4)2(s) + 2 H+(aq)Reaction of cadmium with selenium and selenium compoundsCd reacts with Se when heated rigorously [5].
Cd(s) + Se(s)  CdSe(s) CdSe(s)Cd reacts with H2Se forming CdSe [5]. Cd(s) + H2Se(s)  CdSe(s) + H2(g) CdSe(s) + H2(g)Cd reacts with Se2Cl2 forming CdSe. The reaction is slow and requires heat [5]. Cd(s) + Se2Cl2(s)  CdSe(s) CdSe(s)Reaction of cadmium with sulfidesIn dry air Cd reacts very slowly with H2S forming CdS. The reaction increases with increasing moisture in the air [5].
Cd(s) + H2S(g)  CdS(s) [yellow] CdS(s) [yellow]In strong acids like HCl and H2SO4, Cd2+ is precipitated by H2S as CdS. It should be noted that the precipitate is not pure but a mixture of CdS-CdCl2 or CdS-CdSO4. The H+ to Cd2+ ratio has a maximum above which the purity decreases with increasing [H+]. Besides HCl and H2SO4, precipitations has also been done successfully with KCN and NH4Cl [5]. Cd2+(aq) + H2S(aq)  CdS(s) [yellow] CdS(s) [yellow]In ammonia and cyanide under alkaline conditions, Cd2+ is easily precipitated by S2−: [Cd(NH3)4]2+(aq) + S2−(aq)  CdS(s) [yellow] + 4 NH3(aq) CdS(s) [yellow] + 4 NH3(aq)[Cd(CN)4]2−(aq) + S2−(aq)  CdS(s) [yellow] + 4 CN−(aq) CdS(s) [yellow] + 4 CN−(aq)Reaction of cadmium with sulfurIn gaseous form, Cd and S8 reacts forming CdS. At 130-180 °C solid Cd and S8 reacts explosively, also forming CdS [5].
Cd(g) + S8(g)  CdS(g) CdS(g)Cd(s) + S8(s)  CdS(s) [yellow] CdS(s) [yellow]Reaction of cadmium with sulfuric acidCadmium metal dissolves slowly in dilute sulphuric acid to form Cd(II) ion and hydrogen, H2. In aqueous solution, Cd(II) is present as the complex ion [Cd(H2O)6]2+.
Cd(s) + H2SO4(aq)  Cd2+(aq) + SO42−(aq) + H2(g) Cd2+(aq) + SO42−(aq) + H2(g)Reaction of cadmium with telluriumCd reacts rigorously with Te forming CdTe [5].
Cd(s) + Te(s) ~ 700 °C CdTe(s) Reaction of cadmium with waterCadmium reacts with H2O(g) forming H2(g) at temperatures above 400 °C [5].
Cd(s) + H2O(g)  CdO(s) [Reddish-brown] CdO(s) [Reddish-brown]Cd only reacts very slowly with destilled water (24-48 h for reaction) [5]. Quantitative analysisMethod 3500-Cd C Inductively Coupled Plasma Method [1]. A portion of the sample is digested in a combination of acids. The digest is aspirated into an 8,000 K argon plasma where resulting light emission is quantified for 30 elements simultaneously.
Method limit of detection in water = 0.001 mg/L Method limit of detection in soil = 0.10 mg/kg |